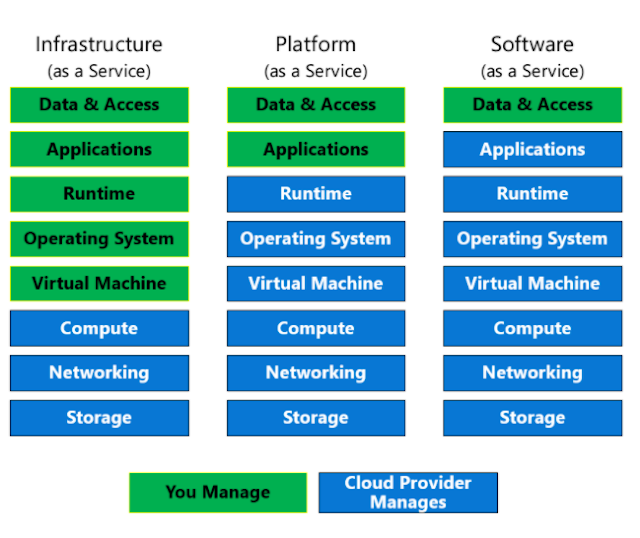
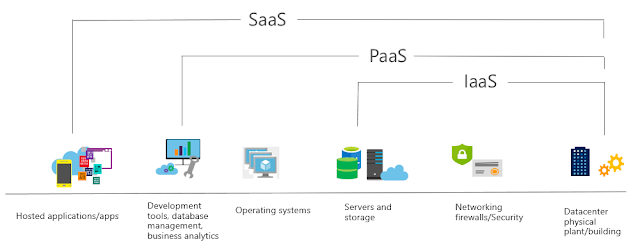
Software as a Service (SaaS) is software that is centrally hosted and managed for the end customer. It allows users to connect to and use cloud-based apps over the internet. Common examples are email, calendars, and office tools such as Microsoft Office 365.
Software as a Service (SaaS) is typically licensed through a monthly or annual subscription, and Office 365 is an example of Software as a Service (SaaS) software.
Software as a Service (SaaS) characteristics
Upfront Costs - Users have no upfront costs; they pay a subscription, typically on a monthly or annual basis.
User Ownership - Users just use the application software; they are not responsible for any maintenance or management of that software.
Cloud Provider Ownership - The cloud provider is responsible for the provision, management, and maintenance of the application software.
Disadvantages of Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software limitations - There may be some limitations to a software application that might affect how users work. Since you are using as-is software you don't have direct control of features. Any business needs and software limitations should be taken into consideration when considering which SaaS platform is best suited for a workload.
Common usage of Software as a Service (SaaS)
Examples of Microsoft Software as a Service (SaaS) services include Office 365, Skype, and Microsoft Dynamics CRM Online.